

Input reset, // Active-high synchronous reset to 32'h1Ĭonsider the n-bit shift register circuit shown below: Connect the Q outputs to the red lights LEDR.īuild a 32-bit Galois LFSR with taps at bit positions 32, 22, 2, and 1.
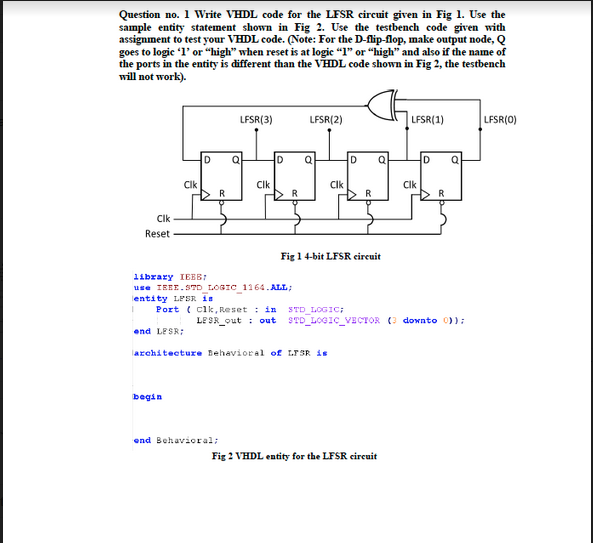
Connect the R inputs to the SW switches, connect Clock to KEY, and L to KEY. Assume that you are going to implement the circuit on the DE1-SoC board. Write the Verilog code for this sequential circuit (Submodules are ok, but the top-level must be named top_module). Note that I drew the XOR gate at position 5 for consistency, but one of the XOR gate inputs is 0.īuild this LFSR. (Tap positions are usually numbered starting from 1). The following diagram shows a 5-bit maximal-length Galois LFSR with taps at bit positions 5 and 3. A maximum-length LFSR of n bits cycles through 2n-1 states before repeating (the all-zero state is never reached).
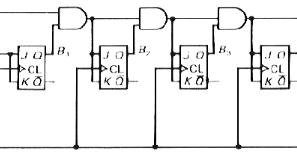
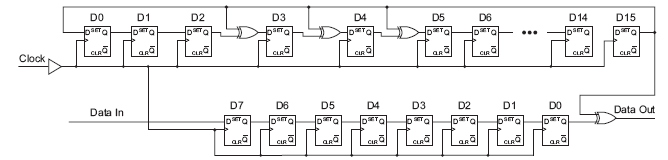
If the taps positions are carefully chosen, the LFSR can be made to be "maximum-length". A Galois LFSR is one particular arrangement where bit positions with a "tap" are XORed with the output bit to produce its next value, while bit positions without a tap shift. amount: Chooses which direction and how much to shift.Ī linear feedback shift registerlinear feedback shift register is a shift register usually with a few XOR gates to produce the next state of the shift register.There is no difference between logical and arithmetic left shifts. Another way of thinking about an arithmetic right shift is that it assumes the number being shifted is signed and preserves the sign, so that arithmetic right shift divides a signed number by a power of two. The shifter can shift both left and right, and by 1 or 8 bit positions, selected by amount.Īn arithmetic right shift shifts in the sign bit of the number in the shift register (q in this case) instead of zero as done by a logical right shift. ena: Chooses whether and which direction to rotate.īuild a 64-bit arithmetic shift register, with synchronous load.load: Loads shift register with data instead of rotating.If enabled, a rotator rotates the bits around and does not modify/discard them. A rotator shifts-in the shifted-out bit from the other end of the register, unlike a shifter that discards the shifted-out bit and shifts in a zero. Output reg clk or posedge areset)beginīuild a 100-bit left/right rotator, with synchronous load and left/right enable. If both the load and ena inputs are asserted (1), the load input has higher priority. ena: Shift right (q becomes zero, q is shifted out and disappears).load: Loads shift register with data instead of shifting.Build a 4-bit shift register (right shift), with asynchronous reset, synchronous load, and enable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
